Transform To Standard Form - If the laplace transform of a signal exists and if the roc includes the jω axis, then the fourier transform is equal to the laplace transform evaluated on the. The fourier transform is the \swiss army knife of. In this chapter we introduce the fourier transform and review some of its basic properties. But just as we use the delta function to accommodate periodic signals, we can. The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform. For a pulse has no characteristic time. The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse.
In this chapter we introduce the fourier transform and review some of its basic properties. For a pulse has no characteristic time. The fourier transform is the \swiss army knife of. But just as we use the delta function to accommodate periodic signals, we can. The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse. If the laplace transform of a signal exists and if the roc includes the jω axis, then the fourier transform is equal to the laplace transform evaluated on the. The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform.
The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform. The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse. In this chapter we introduce the fourier transform and review some of its basic properties. The fourier transform is the \swiss army knife of. But just as we use the delta function to accommodate periodic signals, we can. For a pulse has no characteristic time. If the laplace transform of a signal exists and if the roc includes the jω axis, then the fourier transform is equal to the laplace transform evaluated on the.
Transforming Quadratic Equation into Standard Form (Easy Way) YouTube
In this chapter we introduce the fourier transform and review some of its basic properties. The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform. For a pulse has no characteristic time. The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse. But just as we use the.
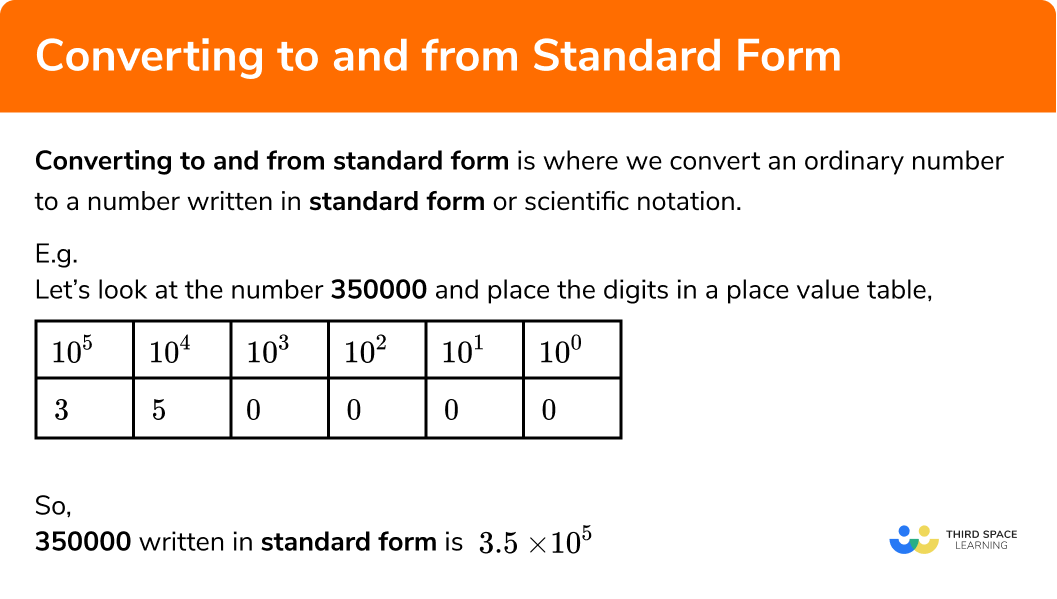
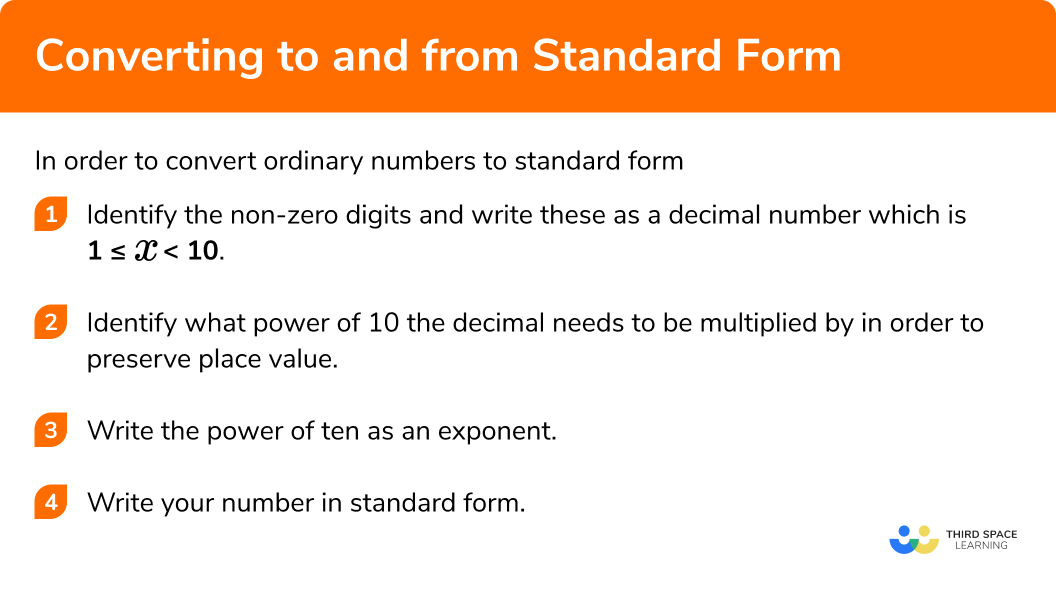
Standard Form GCSE Maths Steps, Examples & Worksheet
If the laplace transform of a signal exists and if the roc includes the jω axis, then the fourier transform is equal to the laplace transform evaluated on the. The fourier transform is the \swiss army knife of. In this chapter we introduce the fourier transform and review some of its basic properties. The unit step function does not converge.
Quadratics Convert to Standard Form Math, Algebra, Quadratic
If the laplace transform of a signal exists and if the roc includes the jω axis, then the fourier transform is equal to the laplace transform evaluated on the. For a pulse has no characteristic time. The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform. The fourier transform is the \swiss army knife of. But just as we.
Quadratic Equation Standard Form Standard Form Of The Quadratic
The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse. If the laplace transform of a signal exists and if the roc includes the jω axis, then the fourier transform is equal to the laplace transform evaluated on the. But just as we use the delta function to accommodate.
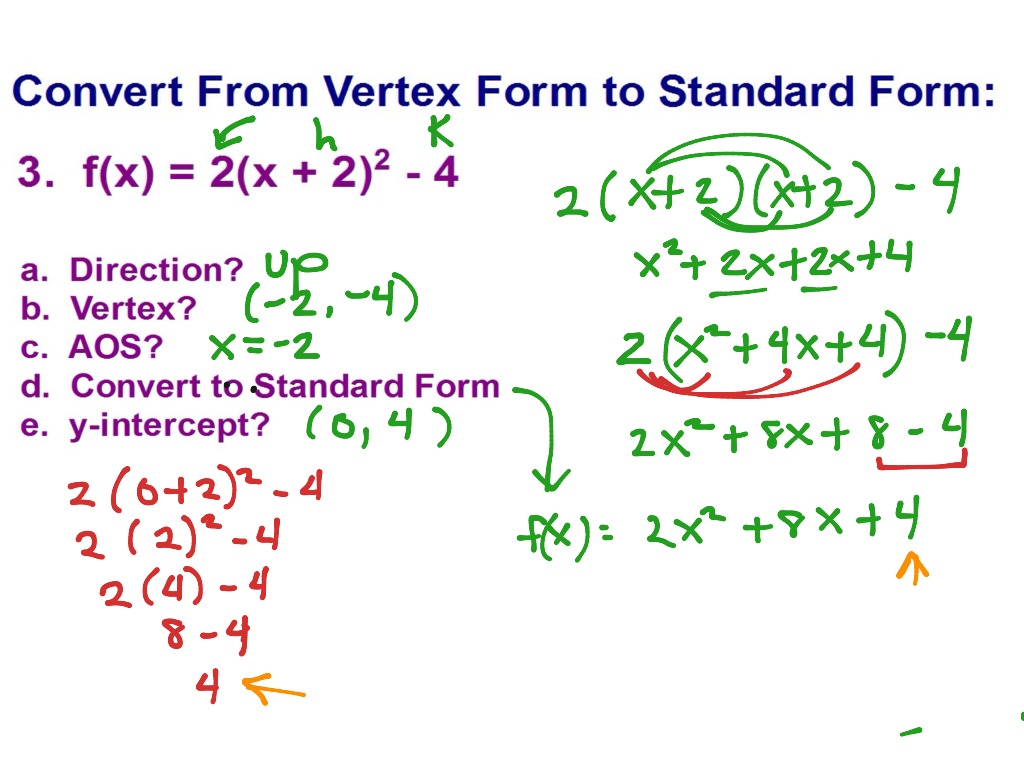
3.4 Vertex to Standard Form ppt download
The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse. But just as we use the delta function to accommodate periodic signals, we can. The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform. The fourier transform is the \swiss army knife of. If the laplace transform of.
Converting Numbers to Standard Form and back YouTube
If the laplace transform of a signal exists and if the roc includes the jω axis, then the fourier transform is equal to the laplace transform evaluated on the. In this chapter we introduce the fourier transform and review some of its basic properties. But just as we use the delta function to accommodate periodic signals, we can. The fourier.
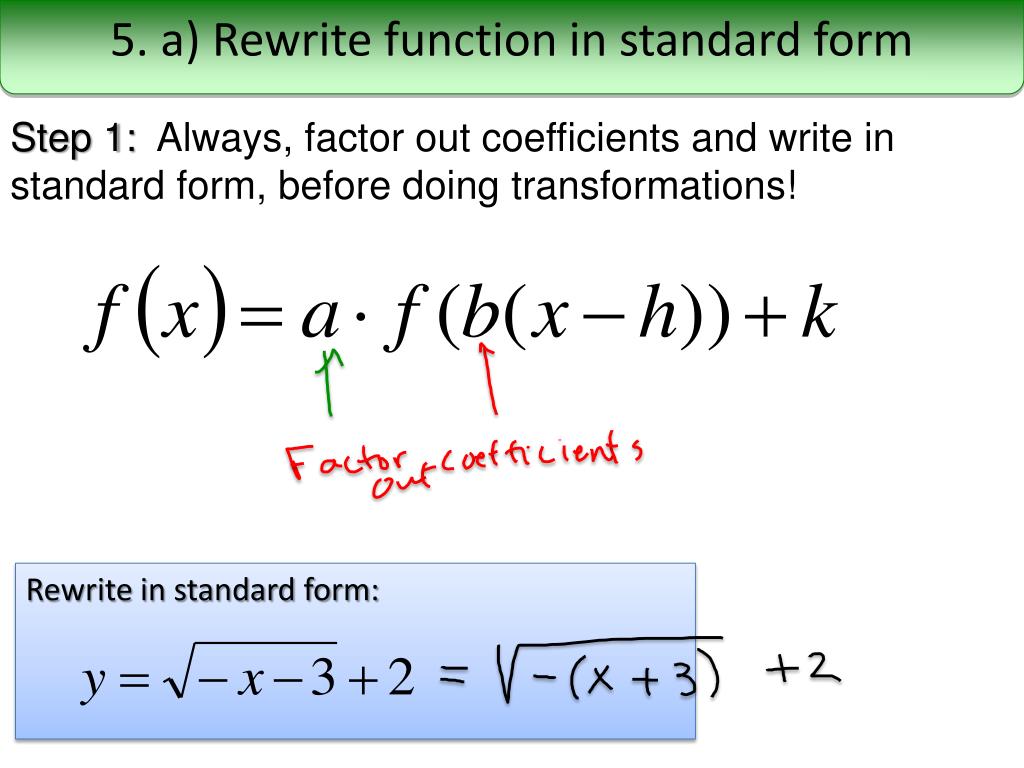
PPT 1. Transformations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
The fourier transform is the \swiss army knife of. The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse. But just as we use the delta function to accommodate periodic signals, we can. The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform. For a pulse has no.
Standard Form GCSE Maths Steps, Examples & Worksheet
But just as we use the delta function to accommodate periodic signals, we can. The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse. The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform. In this chapter we introduce the fourier transform and review some of its basic.
Standard Form of Linear Equations CK12 Foundation
The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse. For a pulse has no characteristic time. If the laplace transform of a signal exists and if the roc includes the jω axis, then the fourier transform is equal to the laplace transform evaluated on the. The unit step.
Lesson 3.7 Standard Form 37 Standard Form ppt download
In this chapter we introduce the fourier transform and review some of its basic properties. The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform. The fourier transform is the \swiss army knife of. The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse. For a pulse has.
But Just As We Use The Delta Function To Accommodate Periodic Signals, We Can.
In this chapter we introduce the fourier transform and review some of its basic properties. The unit step function does not converge under the fourier transform. If the laplace transform of a signal exists and if the roc includes the jω axis, then the fourier transform is equal to the laplace transform evaluated on the. The fourier transform of f ̃(ω) = 1 gives a function f(t) = δ(t) which corresponds to an infinitely sharp pulse.
For A Pulse Has No Characteristic Time.
The fourier transform is the \swiss army knife of.