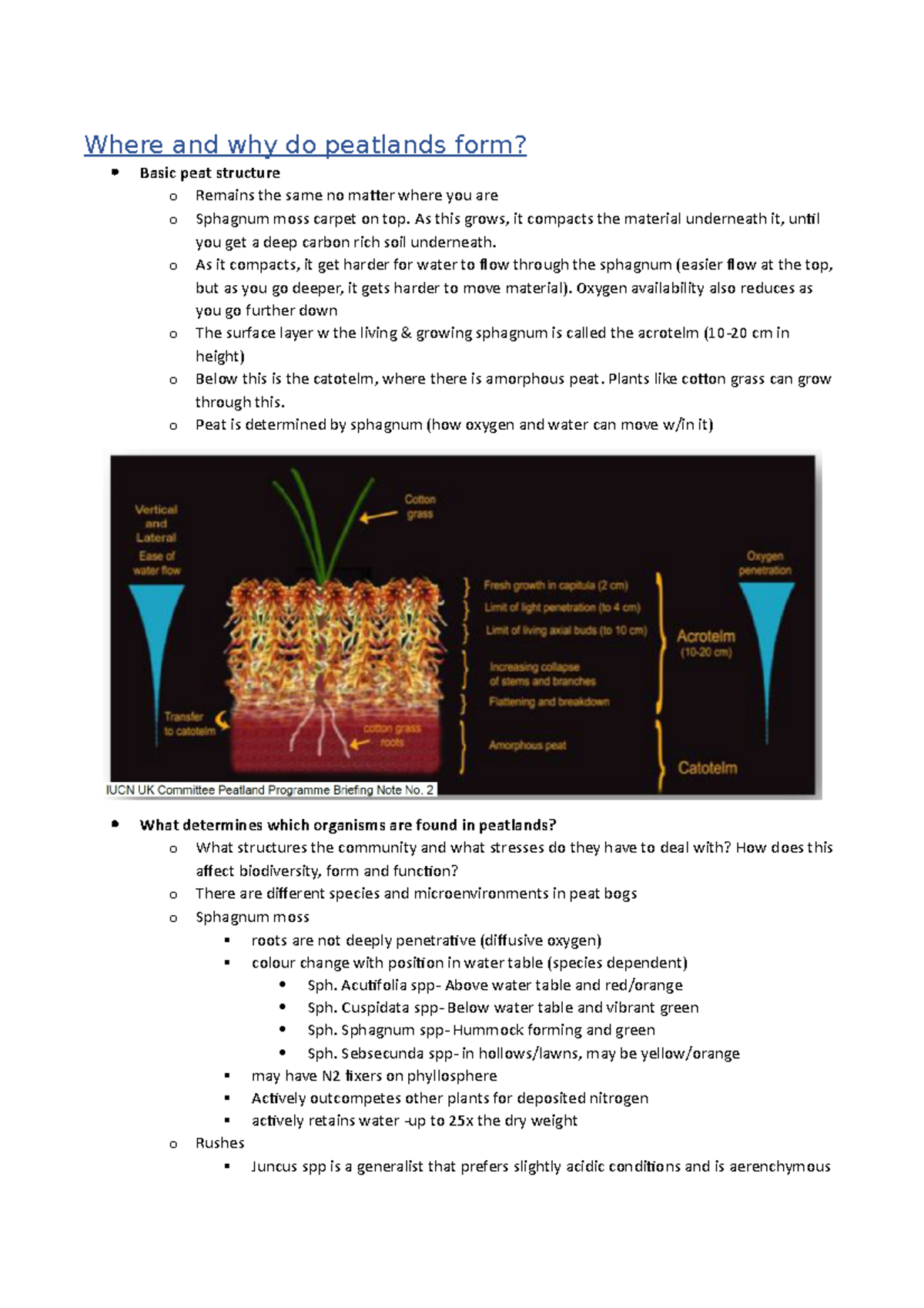
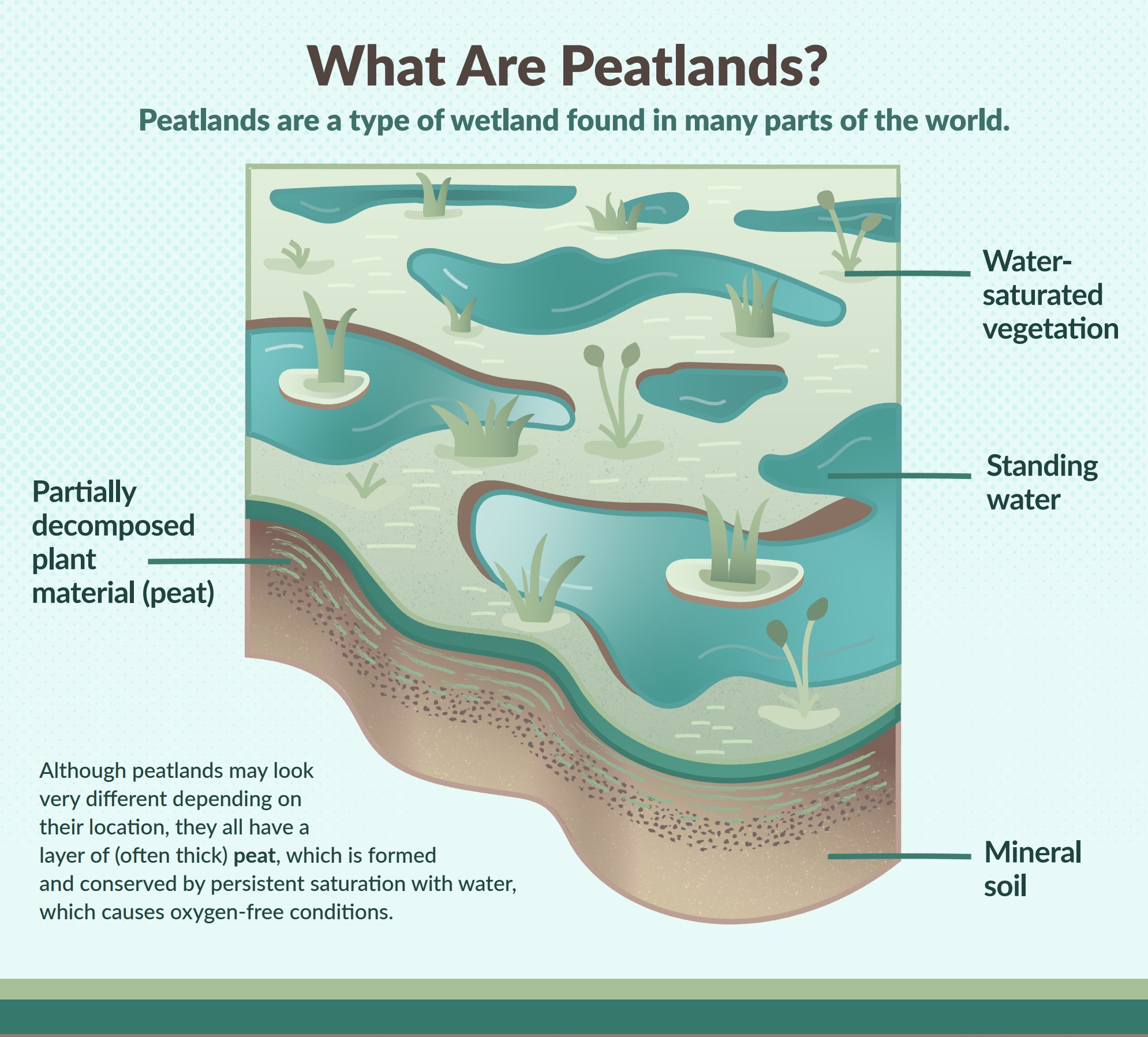
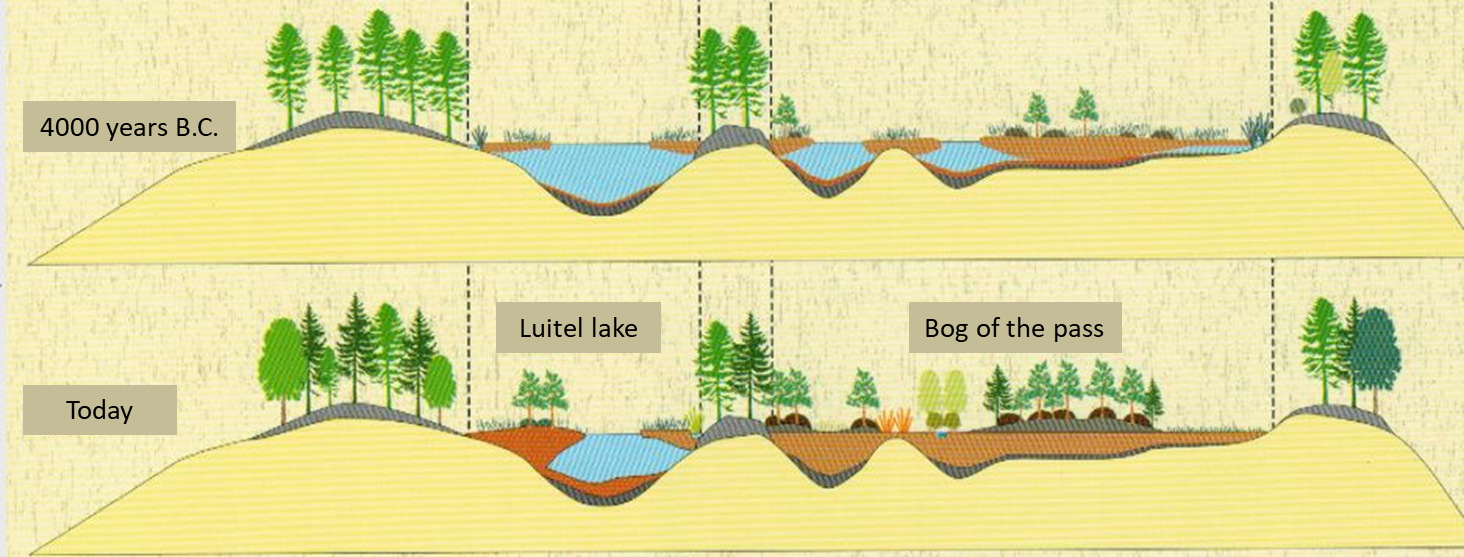
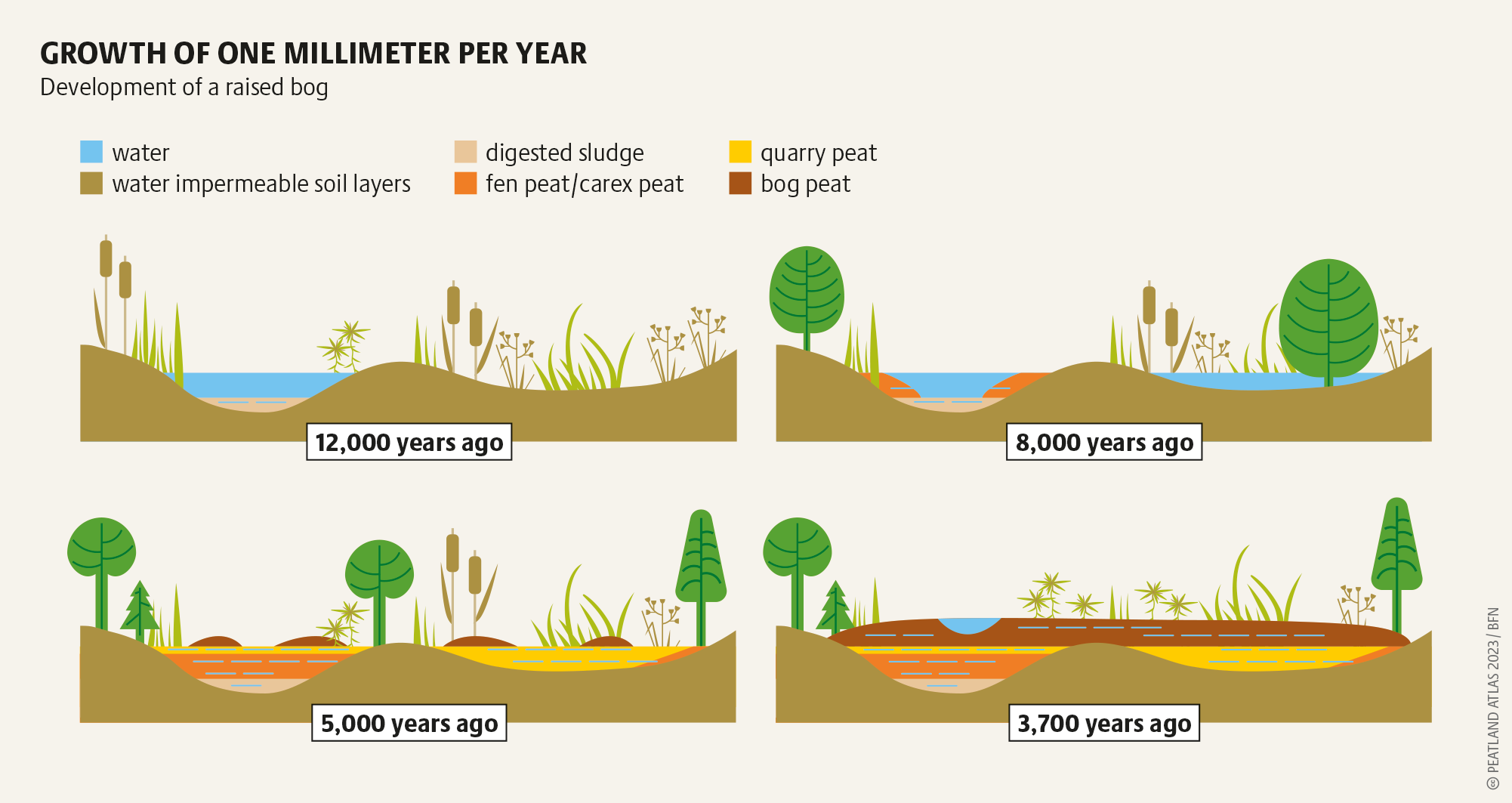
How Are Peatlands Formed - Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. By removing carbon dioxide from the. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface. Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. Peatlands are a type of wetland which accumulates peat, a substance made of partially decomposed organic matter. Peatlands are terrestrial wetland ecosystems in which waterlogged conditions prevent plant material from fully decomposing.
Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. Peatlands are a type of wetland which accumulates peat, a substance made of partially decomposed organic matter. Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface. Peatlands are terrestrial wetland ecosystems in which waterlogged conditions prevent plant material from fully decomposing. By removing carbon dioxide from the.
Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. Peatlands are terrestrial wetland ecosystems in which waterlogged conditions prevent plant material from fully decomposing. By removing carbon dioxide from the. Peatlands are a type of wetland which accumulates peat, a substance made of partially decomposed organic matter. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface.
Peatlands Summer week 34 Where and why do peatlands form? Basic
Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface. Peatlands are terrestrial wetland ecosystems in which waterlogged conditions prevent plant material from fully decomposing. Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. By removing carbon.
Peatlands, Which Can Help Fight Against Climate Change, Face Many
Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. Peatlands are a type of wetland which accumulates peat, a substance made of partially decomposed organic matter. By removing carbon dioxide from the. Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. Peatlands are unusual.
Peatlands and marshes, remarkable wetlands Encyclopedia of the
Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. Peatlands are terrestrial wetland ecosystems in which waterlogged conditions prevent plant material from fully decomposing. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface. Peatlands are wetland.
3 Peat A Porous Medium Groundwater in Peat and Peatlands
By removing carbon dioxide from the. Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. Peatlands are terrestrial wetland ecosystems in which waterlogged conditions prevent plant material from fully decomposing. Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. Peatlands are unusual landforms that.
Formation of tropical peatlands Peatlands form where clima… Flickr
Peatlands are terrestrial wetland ecosystems in which waterlogged conditions prevent plant material from fully decomposing. Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. Peatlands are a type of wetland which accumulates peat, a substance.
Succow Stiftung Peatland Atlas
Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. By removing carbon dioxide from the. Peatlands are a type of wetland which accumulates peat, a substance made of partially decomposed organic matter. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface. Peatlands are a.
CARBON CYCLE 3 peatlands ppt download
Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. By removing carbon dioxide from the. Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and.
Schematic crosssection through a typical tropical peat dome in
Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface. Peatlands are terrestrial wetland ecosystems.
Peat soil fires Campaigners say England's 'rainforests' illegally
Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the. By removing carbon dioxide from the. Peatlands are a type of wetland which accumulates peat, a substance made of partially decomposed organic matter. Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. Peatlands are terrestrial.
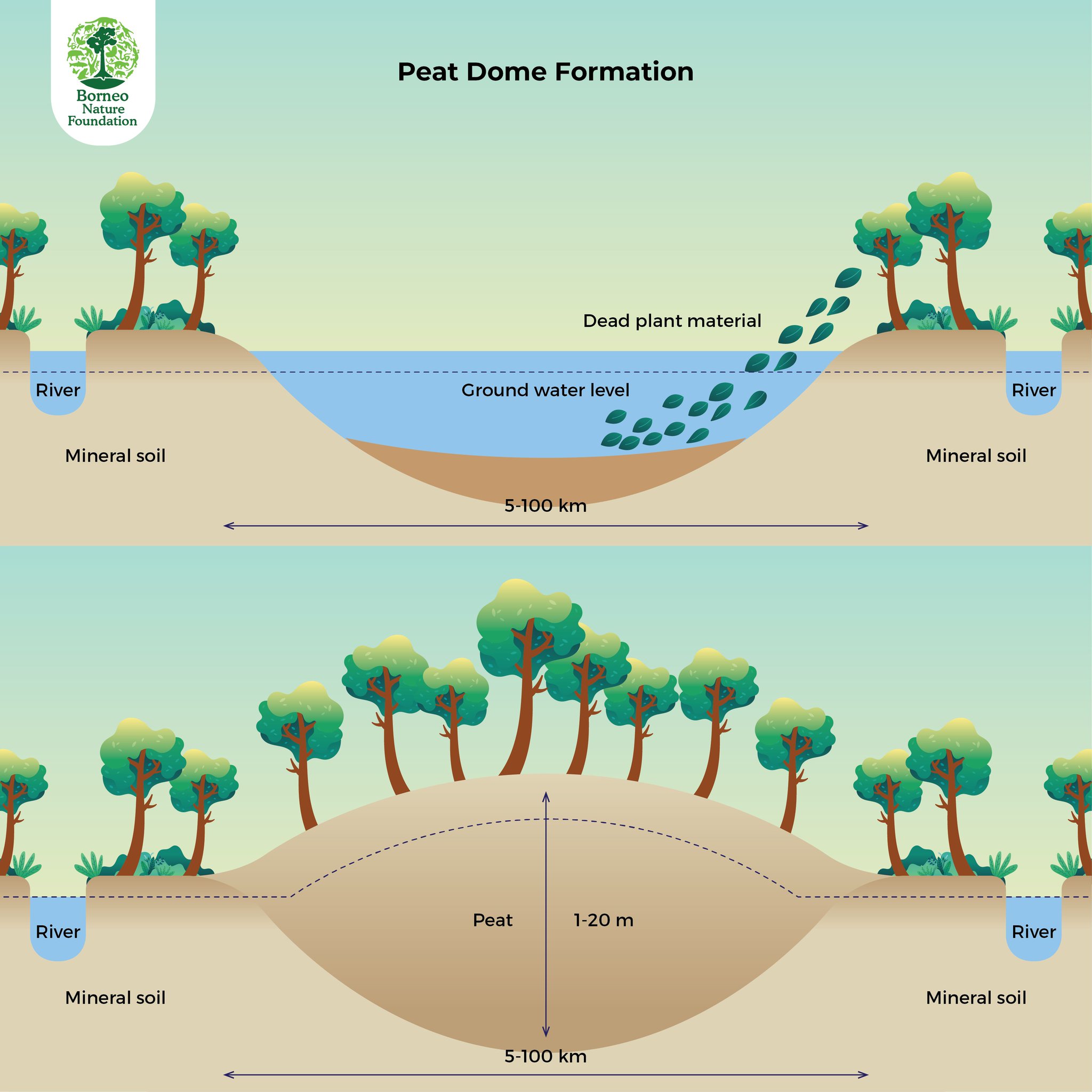
BorneoNatureFdn on Twitter "Do you ever wonder how the peatland formed
Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. Peatlands are unusual landforms that derive mostly from biological rather than physical processes, and can take on characteristic shapes and surface. Peatlands are a type of wetland which accumulates peat, a substance made of partially decomposed organic matter. By removing carbon dioxide from the. Peatlands are a.
Peatlands Are Unusual Landforms That Derive Mostly From Biological Rather Than Physical Processes, And Can Take On Characteristic Shapes And Surface.
Peatlands are wetland ecosystems that store more carbon than any other natural habitat. By removing carbon dioxide from the. Peatlands are terrestrial wetland ecosystems in which waterlogged conditions prevent plant material from fully decomposing. Peatlands are a type of terrestrial wetland ecosystem with a naturally accumulated layer of dead plant material, called peat, at the.